
Automate deployment with Gitlab CI/CD and AWS S3
制作・開発Deploying static sites to AWS S3 can be a tedious repetitive manual process, but with Gitlab CI/CD, you can automate your deployment workflow efficiently.
This guide will walk you through setting up an automated CI/CD pipeline to make your development process more reliable.
静的なサイトを AWS S3 にデプロイするのは面倒な手作業の繰り返しですが、Gitlab CI/CD を使えばデプロイのワークフローを効率的に自動化できます。
このガイドでは、開発プロセスをより信頼性の高いものにするための自動 CI/CD パイプラインのセットアップについて説明します。
What is deployment automation?
デプロイの自動化とは?
Automating deployment is setting up a pipeline that will automatically move your code changes to a server or hosting service, in this case an S3 bucket, whenever you make changes to your code.
デプロイの自動化とは、コードに変更を加えるたびに、コードの変更をサーバーやホスティングサービス(この場合はS3バケット)に自動的に移動するパイプラインを設定することです。
Why automate deployment?
なぜデプロイを自動化するのか?
Automating deployment offers numerous advantages that enhance the development process. Some of these include:
- Reduced manual effort: it allows you to focus on coding while it takes care of the files update
- Enhanced speed: it speeds up the deployment process for faster, more frequent updates
- Minimized errors: it’s less prone to human error, leading to more reliable deployments
- Continuous delivery: always in a deployable state. Every change made is automatically ready for deployment at any time
デプロイの自動化には、開発プロセスを強する数多くの利点があります。下記がその例です:
- 手作業の削減:ファイルの更新を処理する間、コーディングに専念できます。
- スピードの向上: デプロイプロセスが高速化され、より迅速で頻繁なアップデートが可能になります。
- エラーの最小化: 人為的なミスが減り、より信頼性の高いデプロイが可能になります。
- 継続的デリバリー: 常にデプロイ可能な状態を保ちます。すべての変更が自動的にいつでもデプロイ可能な状態になります。
How to automate deployment?
デプロイを自動化する方法は?
To automate deployment, there are few steps to be performed both on the AWS side and the Gitlab side. Let’s go through them デプロイを自動化するには、AWS側とGitlab側の両方でいくつかの手順を実行する必要があります。それでは見ていきましょう:
The AWS side
AWS側
For the pipeline to access your S3 bucket, you will need to have an IAM user with the necessary permissions.
- Go to the AWS Management Console
- Navigate to Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Create a new user with the AmazonS3FullAccess managed policy, or create a custom policy tailored to your specific needs
- Follow the prompts to create the user and generate access keys (Access Key ID and Secret Access Key) that will be used later on.
パイプラインがS3バケットにアクセスするには、必要な権限を持つIAMユーザーが必要です。
- AWSマネジメントコンソールに移動
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)に移動する
- AmazonS3FullAccessマネージドポリシーで新規ユーザーを作成するか、特定のニーズに合わせたカスタムポリシーを作成する
- 画面の指示に従ってユーザーを作成し、後で使用するアクセスキー(アクセスキーIDとシークレットアクセスキー)を生成する。
The Gitlab side
Gitlab側
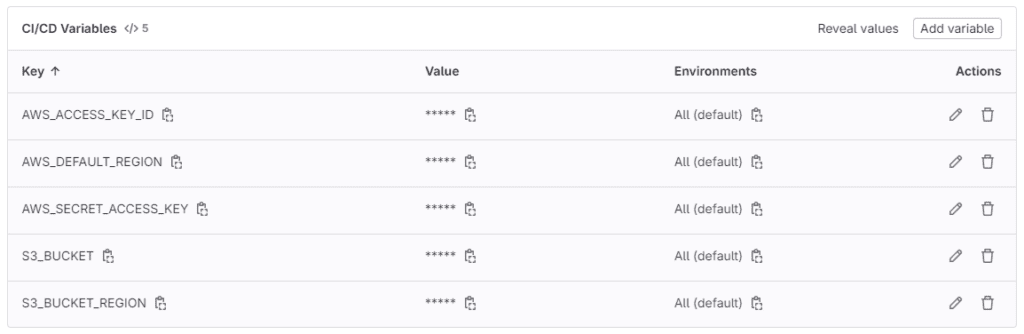
On the Gitlab side, start by setting the necessary variables within your existing Gitlab project. To do this, go to Settings → CI/CD
You will need to add the following variables:
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: this is the Access Key generated in the previous step
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: this the Secret Access Key generated in the previous step
- AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: this is the default region of your AWS account, usually found on the top right of the AWS Management Console
- S3_BUCKET: this variable will hold the name of your S3 bucket.
Gitlab側では、まず既存のGitlabプロジェクトに必要な変数を設定します。Settings → CI/CDに設定してください。
以下の変数を追加する必要があります:
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: 前のステップで生成されたアクセスキーです。
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: 前のステップで生成されたシークレットアクセスキーです。
- AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: AWSアカウントのデフォルトリージョンで、通常はAWSマネジメントコンソールの右上に表示されます。
- S3_BUCKET: この変数にはS3バケットの名前が入ります。
If your S3 bucket is in a different region from the AWS default region, as in the example below, you need to create an additional variable S3_BUCKET_REGION to store the region information.
下記の例のように、S3バケットがAWSのデフォルトリージョンと異なるリージョンにある場合、リージョン情報を格納するために追加の変数S3_BUCKET_REGIONを作成する必要があります。
The CI/CD variables should look something like this CI/CD変数は次のようになるはずです:
Creating the .gitlab-ci.yml file
.gitlab-ci.ymlファイルの作成
Now you’re ready to write your .gitlab-ci.yml file. This file defines the CI/CD pipeline stages, and the steps to deploy your files.
これで .gitlab-ci.yml ファイルの作成準備が整いました。このファイルでは、CI/CDパイプラインのステージとファイルをデプロイする手順を定義します。
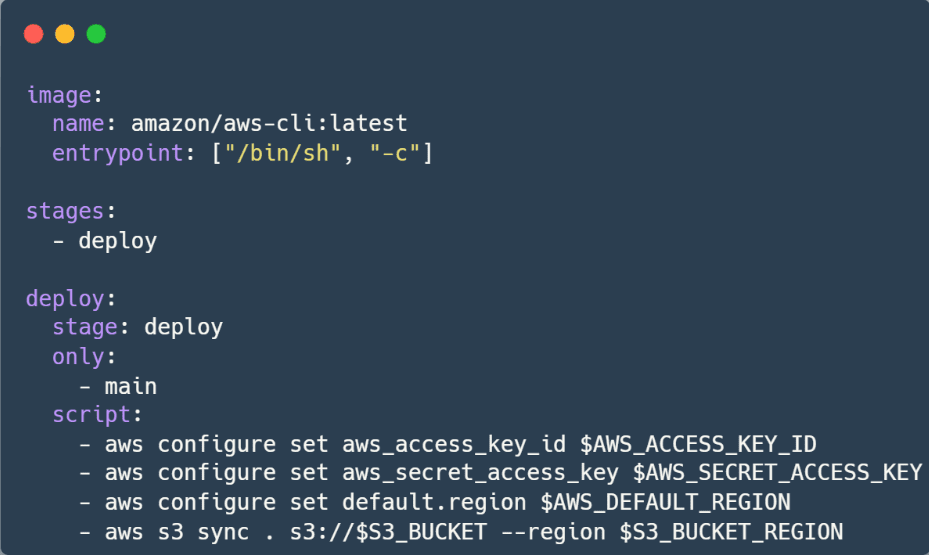
Let’s break down the above code.
- image: specifies the Docker image to use, in our case, it’s the latest AWS CLI.
- entrypoint: to ensure that commands are executed in a shell
- stages: defines the pipeline stages. You can name the stages however you see fit. In this example, we use a single stage named deploy.
- Deploy:
- stage: specifies the stage this job belongs to
- only: specifies the branch this job should run on, here “main” branch
- script: the commands to be executed. It starts by setting AWS CLI with the provided information, then syncing the repository content to the specified S3 bucket.
上のコードを分解してみましょう。
- image: 使用するDockerイメージを指定します。この場合は最新のAWS CLIです。
- entrypoint: コマンドがシェルで実行されるようにします。
- stages: パイプラインのステージを定義します。ステージの名前は自由につけることができます。この例では、deployという1つのステージを使っています。
- デプロイ:
- stage: このジョブが属するステージを指定します。
- only: このジョブが実行されるブランチを指定します。ここでは 「main」 ブランチです。
- script: 実行するコマンドを指定します。提供された情報でAWS CLIを設定することから始まり、指定されたS3バケットにリポジトリの内容を同期します。
Testing
テスト
To confirm your changes, push your code to your Gitlab branch and verify that the pipeline passes successfully. This ensures that the automated deployment process was set up correctly.
変更を確認するには、コードを Gitlab ブランチにプッシュし、パイプラインが正常に通過することを確認します。これで、自動デプロイメントプロセスが正しく設定されたことが確認できます。
